2022年交通银行秋季招聘试卷
题目总数:100
总分数:100
时间:不限时
第 1 题
单选题
在共享充电宝市场中,无线充电模式已经有企业在做了,这是其在技术上的优势。苹果、三星均在进行无线充电技术的研发应用,相信不久就会有产品使用这项技术,而国产机型也不会差到哪儿去。可以预料,未来无线充电必然是大趋势,而只要技术相对成熟是可以应用到所有的移动设备中去的。如果你的共享充电技术不能跟上的话,即便是处于市场领先的地位也会被抛弃。在技术水平相同的情况下,市场和用户是首选,而事关到技术层次,当然是更高一级的会直接取代旧的技术产品,类似于无线充电技术和长续航的电池技术就属于高纬度的技术层级。
对这段文字概括最准确的是( )。
对这段文字概括最准确的是( )。
A.
无线充电技术在共享充电宝上的应用已经迫在眉睫
B.
技术水平是保证市场地位的首要条件
C.
技术创新和市场争夺同等重要,不能顾此失彼
D.
无线充电技术将成为未来共享充电宝的标配
第 2 题
单选题
海洋刚形成时,海底热液活动的强度是现今强度的5倍。广泛并剧烈的海底热液活动导致了地球内部热量的散逸以及大量还原性金属元素和气体的产生。因此,那个时候的海洋处于强还原环境,富含还原态的铁、铜、锌、铅、锰等金属离子,以及甲烷、氢气和硫化氢等气体,海水的温度维持在70~100℃。由于光合作用还没有出现,大气中几乎不含氧气,二氧化碳的含量很高,因而海洋呈酸性。不难看出,早期海洋所具有的环境与现代海底热液喷口周围的环境非常相似。科学家猜想,正是在早期海洋海底热液喷口周围,生命开始悄悄地萌芽了。
针对以上文段,下列各项说法正确的是( )。
针对以上文段,下列各项说法正确的是( )。
A.
早期海洋环境不适合生物生存
B.
二氧化碳的含量影响海洋酸碱度
C.
现代海洋海底热液喷口也在产生着新物种
D.
现在海洋中不再含有甲烷、氢气和硫化氢等气体
第 3 题
单选题
下列各句中没有语病,句意明确的是( )。
A.
红队对于蓝队的进攻早有防备,采取迂回战术迅速化解了危机。
B.
假期结束后在员工中存在的“放假综合症”问题,总经理表示可以理解。
C.
他深情地看着怀里熟睡的婴儿,那是这个家族传承的希望。
D.
全球化不仅为我国经济带来了积极的影响,而且我国的特色社会主义市场经济体制也使我们在竞争中更有优势。
第 4 题
单选题
建设腾格里南缘生态屏障需要________谋划实施生态农业________工程、循环经济示范园区工程等一批重大生态产业培育工程,打造沙漠南缘生态产业屏障。
填入画横线部分最恰当的一组是( )。
填入画横线部分最恰当的一组是( )。
A.
协同 扶植
B.
协作 扶植
C.
协同 扶持
D.
协作 扶持
第 5 题
单选题
将下列各句重新排列,语序最连贯的一项是( )。
(1)为汽车所有者和移动服务用户二者提供优化的数字解决方案
(2)这是汽车行业颠覆性的、挑战思维定式的发展
(3)“互联出行”可定义为“通过技术将人员和货物从A地移动到B地的按需移动服务”
(4)传统汽车制造商必须拓宽关注点,从产品(汽车)到产品外的实用工具,并且创造出一种商业模型和数字生态系统
(5)它需要彻底重新思考为市场提供价值的方式
(1)为汽车所有者和移动服务用户二者提供优化的数字解决方案
(2)这是汽车行业颠覆性的、挑战思维定式的发展
(3)“互联出行”可定义为“通过技术将人员和货物从A地移动到B地的按需移动服务”
(4)传统汽车制造商必须拓宽关注点,从产品(汽车)到产品外的实用工具,并且创造出一种商业模型和数字生态系统
(5)它需要彻底重新思考为市场提供价值的方式
A.
(4)(5)(3)(2)(1)
B.
(4)(2)(5)(1)(3)
C.
(3)(5)(2)(4)(1)
D.
(3)(2)(5)(4)(1)
第 6 题
单选题
-2, 0, 1, 8, 63, ( )
A.
796
B.
624
C.
1211
D.
127
第 7 题
单选题

A.

B.

C.

D.
第 8 题
单选题
美国前总统林肯曾经说过:最高明的骗子,可能在某个时刻欺骗所有人,也可能在所有的时刻欺骗某些人,但不可能在所有的时刻欺骗所有的人。这个世界上当然存在一些高明的骗子。
读到这段话之后,甲、乙、丙、丁四人分别说了自己的理解。
甲:这就是说,乙可能在某个时刻受骗。
乙:这就是说,丙可能在任何时候都不受骗。
丙:这就是说,不存在某一时刻所有的人都不会受骗。
丁:这就是说,不存在某一时刻有人可能不受骗。
那么,四人所说的话里不一定为假的有几人?( )
读到这段话之后,甲、乙、丙、丁四人分别说了自己的理解。
甲:这就是说,乙可能在某个时刻受骗。
乙:这就是说,丙可能在任何时候都不受骗。
丙:这就是说,不存在某一时刻所有的人都不会受骗。
丁:这就是说,不存在某一时刻有人可能不受骗。
那么,四人所说的话里不一定为假的有几人?( )
A.
4
B.
3
C.
2
D.
1
第 9 题
单选题
某个班级里有45名学生,甲、乙、丙是这个班级里的三个学生。甲:我们班里有些人是转校生;乙:我知道,学习委员是转校生;丙:我们班里有些人不是转校生。他们三个人中只有一个人说对了。
那么,下列说法中正确的是( )。
那么,下列说法中正确的是( )。
A.
45个人都不是转校生
B.
只有一个人是转校生
C.
只有一个人不是转校生
D.
45个人都是转校生
第 10 题
单选题
-1, 1, 2, 2, 5, 4, 8, ( ), 11, 16
A.
12
B.
10
C.
9
D.
8
第 11 题
单选题
只要学生努力学习并且有得当的表扬,学生就能取得好成绩。小贾是学生,但他没有取得好成绩。
据此可知,以下推断正确的是( )。
据此可知,以下推断正确的是( )。
A.
小贾没有取得好成绩,是因为没有得到得当的表扬
B.
造成小贾现状的原因不是他不努力,那么一定是没有得到得当的表扬
C.
如果没有得到得当的表扬,那么,不努力一定是没有取得好成绩的原因
D.
小贾没有取得好成绩,是因为他不够努力
第 12 题
单选题
1, 1.5, 2.4, 4, 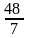 , 12, ( )
, 12, ( )
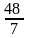 , 12, ( )
, 12, ( )
A.
18
B.
27
C.
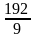
D.
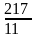
第 13 题
单选题
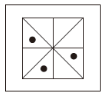
根据规律,填入问号处的图片是( )。
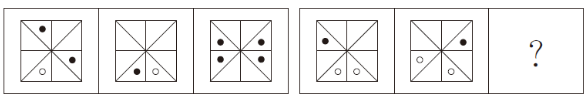

A.
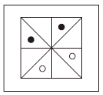
B.
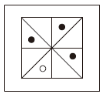
C.
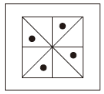
D.
第 14 题
单选题
运动会上,学生们排方阵,排成三层空心方阵的话,就会多出12人,如果在中心再增加一层,那么又少8人。那么排方阵的共有多少名学生?( )
A.
120
B.
110
C.
128
D.
104
第 15 题
单选题
校学生会主席改选中,需要得到总人数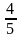 的选票才能当选。统计了
的选票才能当选。统计了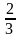 的选票时,小明得到的选票数量已经达到了当前统计票数的
的选票时,小明得到的选票数量已经达到了当前统计票数的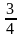 ,他还要得到剩下的几分之几才能达到当选标准?( )
,他还要得到剩下的几分之几才能达到当选标准?( )
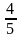 的选票才能当选。统计了
的选票才能当选。统计了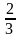 的选票时,小明得到的选票数量已经达到了当前统计票数的
的选票时,小明得到的选票数量已经达到了当前统计票数的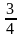 ,他还要得到剩下的几分之几才能达到当选标准?( )
,他还要得到剩下的几分之几才能达到当选标准?( )
A.

B.
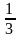
C.
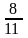
D.
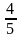
第 16 题
单选题
若160块糖分给110个大人和孩子,其中,每个孩子得3块糖,每个大人得1块糖。那么孩子的人数是多少?( )
A.
15人
B.
18人
C.
21人
D.
25人
第 17 题
单选题
一次海边素质拓展活动中,所有人分成了甲、乙、丙、丁四个组。计划收集若干贝壳。甲队的数额是另外三队总和的一半。乙队的数额是另外三队总和的三分之一。丙队的数额是另外三队总和的四分之一,丁队的数额是130个。那么甲团队的数额是多少个?( )
A.
200
B.
300
C.
400
D.
500
第 18 题
单选题
某商品原价若干元,现在降价3元。购买人数增加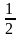 ,收入增加20%,那么商品原价多少元?( )
,收入增加20%,那么商品原价多少元?( )
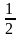 ,收入增加20%,那么商品原价多少元?( )
,收入增加20%,那么商品原价多少元?( )
A.
15
B.
20
C.
10
D.
25
第 19 题
单选题
一项关于运动、读书、音乐三项爱好调查中,喜欢运动的有49人,喜欢读书的有36人,喜欢音乐的有28人;只喜欢其中两项的有13人,喜欢三项的有9人。那么被调查的总人数是多少人?( )
A.
82
B.
87
C.
77
D.
92
第 20 题
单选题
小军和小亮共有126本课外读物。如果小军给小亮3本,那么小军的课外读物数量是小亮的2倍,那么小军有课外读物多少本?( )
A.
84
B.
87
C.
89
D.
92
第 21 题
单选题
某幼儿园有一、二、三、四共四个班级。一班人数是所有人数的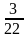 。二班人数是一班人数的
。二班人数是一班人数的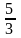 ,三班人数与前两个班级人数和相等,四班比三班少10人。那么这个幼儿园四个班级共有多少人?( )
,三班人数与前两个班级人数和相等,四班比三班少10人。那么这个幼儿园四个班级共有多少人?( )
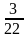 。二班人数是一班人数的
。二班人数是一班人数的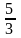 ,三班人数与前两个班级人数和相等,四班比三班少10人。那么这个幼儿园四个班级共有多少人?( )
,三班人数与前两个班级人数和相等,四班比三班少10人。那么这个幼儿园四个班级共有多少人?( )
A.
160
B.
150
C.
110
D.
90
第 22 题
单选题
某班级学生分别来自甲、乙、丙、丁四个地方中的其中一个,统计发现,10%的学生来自甲,28%的学生来自乙。来自丙、丁的人数是一样的,那么,来自乙地的学生人数比来自丙地的人数( )。
A.
多10.7%
B.
少10.7%
C.
少9.7%
D.
多9.7%
第 23 题
单选题
将溶液倒入若干个瓶子中,如果每瓶装3 500毫升,那么还剩下5 000毫升。如果每瓶装4 000毫升,那么还剩下500毫升,那么这些瓶子一共多少个?( )
A.
9
B.
10
C.
11
D.
12
第 24 题
单选题
甲是乙目前年龄的时候,乙12岁;如果乙是甲现在年龄的话,甲51岁。那么现在甲多少岁?( )
A.
38
B.
48
C.
25
D.
59
第 25 题
单选题
某幼儿园组织学生排成一队前往甲地。学生每分钟步行30米。队尾的苗老师以每分钟步行50米的速度赶到队首。然后立即返回队尾,用了5分钟,那么,队伍的长度是( )米。
A.
80
B.
100
C.
60
D.
120
第 26 题
单选题
某大学外文系学生中男生占20%,电子系学生中男生占60%,如果合计两个系学生,则男生占48%,那么,外文系学生总人数与电子系学生总人数的比值为( )。
A.
2∶9
B.
3∶7
C.
1∶1
D.
4∶5
第 27 题
单选题
在一次比赛中,要把20位参赛者分成数量不等的4组,那么,一个组最多由几位参赛者组成?( )
A.
11
B.
12
C.
13
D.
14
第 28 题
单选题
某月有31天,且本月有5个星期日,那么,下面日期不可能是星期日的是( )。
A.
4号
B.
3号
C.
2号
D.
1号
第 29 题
单选题
下面是一个三行三列的数字阵型,填入问号处的数字为( )。


A.
7
B.
5
C.
9
D.
3
第 30 题
单选题
因某款服装第一季度供不应求,第二季度该款服装进货价格比第一季度增加了10%,但仍保持原售价。因此,每份利润下降了25%,那么第一季度此款衣服的成本与售价的比是( )。
A.
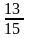
B.
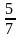
C.
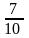
D.
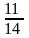
第 31 题
单选题
甲、乙两人共同加工1 300个零件,甲加工一个需要5分钟,乙加工一个需要8分钟。完成任务时,甲加工了多少个零件?( )
A.
1 000
B.
800
C.
500
D.
300
第 32 题
单选题
加工一批零件,如果每天做5个,则比计划晚2天;如果每天做6个,则比计划提前3天。那么这批零件一共( )个。
A.
60
B.
120
C.
28
D.
150
第 33 题
单选题
小明家与县城之间的距离是20千米,他从家出发以4千米/时的速度走了一段路后,搭乘上公交车,公交车的速度是10千米/时。从家出发到县城一共用了3.5小时,那么,小明步行了( )千米。
A.
12
B.
10
C.
8
D.
4
第 34 题
单选题
天宇公司今年的利润额比去年增加了50%,股东分红240万元后,还剩下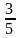 ,那么去年的利润额是( )万元。
,那么去年的利润额是( )万元。
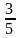 ,那么去年的利润额是( )万元。
,那么去年的利润额是( )万元。
A.
400
B.
500
C.
300
D.
600
第 35 题
单选题
甲、乙、丙、丁四个人多年后相遇,年龄分别是36、38、34、40。甲说:“记得几年前,我和乙、丁的年龄和是丙的4倍。”那么甲说的几年前是多少年前?( )
A.
22
B.
18
C.
12
D.
8
第 36 题
单选题
有大、小车各一辆运送一批180立方米的渣土。大车每次运30立方米,往返一次耗油2升;小车每次运18立方米,往返一次耗油1升,为了省油,最佳方案是( )。
A.
大车运3次,其他让小车运
B.
大车运4次,其他让小车运
C.
大车运5次,其他让小车运
D.
大车运6次,其他让小车运
第 37 题
单选题
研发部、技术部和财务部比赛掰手腕。规则是每队各派出一人掰手腕,胜者再与另一队选手对决,两人对决中,胜者计+1分,败者计-1分,依次循环。最后,得分情况是研发部:+7,-6;技术部:+5,-3;财务部:+3,?。那么财务部败了几场?( )
A.
9
B.
8
C.
7
D.
6
第 38 题
单选题
54.59+23.4×5.3-18.4×5.3-75.79=( )。
A.
1
B.
5.3
C.
0
D.
10.3
第 39 题
单选题
(1+21+48+56+89)×(1+21+48+56+89+21+48+56+89+1)-(21+48+56+89)×(21+48+56+89+1+21+48+56+89+1)=( )。
A.
430
B.
450
C.
1
D.
0
第 40 题
单选题
幼儿园的老师有28颗荧光星星,每天他都会把它们奖励给表现好的小朋友。如果要求每天奖励的星星数量不等,而且不能不奖励,那么,这些星星最多可以用几天?( )
A.
5
B.
6
C.
4
D.
7
第 41 题
单选题
塑料污染对地球环境的破坏日益严重,因此积极采取措施解决这个问题已经迫在眉睫。一种较为方便的方法是塑料垃圾回收,但这种方法不够有效,科学家们一直在想方设法解决塑料污染问题,现在他们发现粉虫或许可以发挥作用。
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
这篇文章要讨论的问题是:
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
这篇文章要讨论的问题是:
A.
塑料污染日益严重地破坏地球环境
B.
粉虫可以解决塑料污染问题
C.
面对塑料污染,粉虫或许是一种解决方案
D.
粉虫与塑料污染之间的关系
第 42 题
单选题
塑料污染对地球环境的破坏日益严重,因此积极采取措施解决这个问题已经迫在眉睫。一种较为方便的方法是塑料垃圾回收,但这种方法不够有效,科学家们一直在想方设法解决塑料污染问题,现在他们发现粉虫或许可以发挥作用。
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
由文中描述可知,经过粉虫加工处理,确定塑料可以变成哪种物质?
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
由文中描述可知,经过粉虫加工处理,确定塑料可以变成哪种物质?
A.
二氧化碳 粪便
B.
二氧化碳 蛋白质
C.
粪便 蛋白质
D.
二氧化碳 某种气体
第 43 题
单选题
塑料污染对地球环境的破坏日益严重,因此积极采取措施解决这个问题已经迫在眉睫。一种较为方便的方法是塑料垃圾回收,但这种方法不够有效,科学家们一直在想方设法解决塑料污染问题,现在他们发现粉虫或许可以发挥作用。
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
珍娜·詹贝克的研究在文中的作用是什么?( )
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
珍娜·詹贝克的研究在文中的作用是什么?( )
A.
说明研究粉虫来处理塑料的事情是有意义的
B.
说明在全球范围内,塑料污染已经成为很大的问题
C.
说明塑料会影响整个生态环境,甚至是人类的健康
D.
说明海洋才是塑料污染最严重的地方
第 44 题
单选题
塑料污染对地球环境的破坏日益严重,因此积极采取措施解决这个问题已经迫在眉睫。一种较为方便的方法是塑料垃圾回收,但这种方法不够有效,科学家们一直在想方设法解决塑料污染问题,现在他们发现粉虫或许可以发挥作用。
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组的目的是什么?( )
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组的目的是什么?( )
A.
增加实验成功的概率
B.
减少粉虫死亡的数量
C.
控制影响粉虫生存的条件
D.
对比不同食物配比下粉虫的生存状况
第 45 题
单选题
塑料污染对地球环境的破坏日益严重,因此积极采取措施解决这个问题已经迫在眉睫。一种较为方便的方法是塑料垃圾回收,但这种方法不够有效,科学家们一直在想方设法解决塑料污染问题,现在他们发现粉虫或许可以发挥作用。
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
研究粉虫的意义在于( )。
(1)可以消耗大量的塑料污染
(2)可以提供丰富的动物蛋白质
(3)可以平衡整个生态系统
《环境科学与技术》上发表的一项研究称,粉虫能够消化塑料,将塑料转化为二氧化碳,而不是如《经济学人》所报道的那样转化为粪便排出体外。研究发现,粉虫消化道中有一种细菌,可以帮助其迅速降解聚合物。其他研究还发现,粉虫还可以消化聚苯乙烯塑料。
当前这项研究显得尤其重要,因为塑料正在给环境及人类健康造成越来越多的负面影响。环境工程师珍娜·詹贝克曾在2015年就这个话题开展了一项研究,她发现,每年约有190亿磅塑料进入海洋,预计到2025年数字会翻倍。塑料会威胁整个生态环境,造成更多动物死亡,而塑料微粒进入食物链,则会给人类带来健康风险。
研究人员将粉虫分成多个小组。几组粉虫以1.8克聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯和两种塑料的混合物为食物,其他几组则以塑料搭配麦麸为食。在为期32天的试验结束时,粉虫的存活率超过90%——麦麸搭配塑料的小组存活率最高。食用聚乙烯的粉虫可将50%的塑料转化为气体,对聚苯乙烯的转化率为45%。
粉虫不仅有助于解决塑料污染危机,也是应对全球粮食危机的一种重要工具。法国农业科学家安东尼·休伯特一直在培育粉虫,制作成“高蛋白”饲料,用于饲养动物和养鱼,最终变成人类餐桌上的美食。休伯特称,粉虫制成的饲料“蛋白质含量非常高”,而且对于动物是健康的。另外,这种饲料对环境也有积极的影响。因为传统动物饲养的二氧化碳排放量,约占全球总排放量的25%。
研究粉虫的意义在于( )。
(1)可以消耗大量的塑料污染
(2)可以提供丰富的动物蛋白质
(3)可以平衡整个生态系统
A.
只有(1)和(2)
B.
只有(1)和(3)
C.
只有(2)和(3)
D.
只有(1)、(2)和(3)
第 46 题
单选题
上海人口老龄化现状和预判
一、上海人口老龄化现状
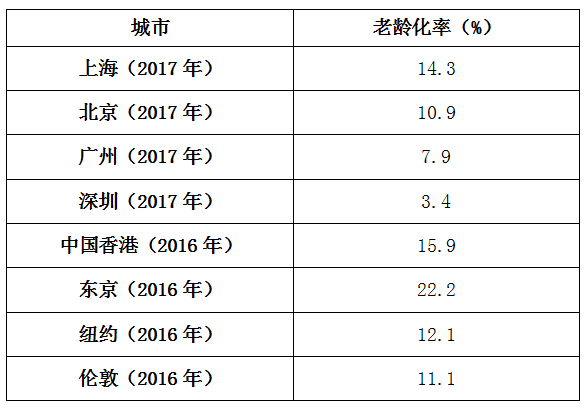
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度
上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。
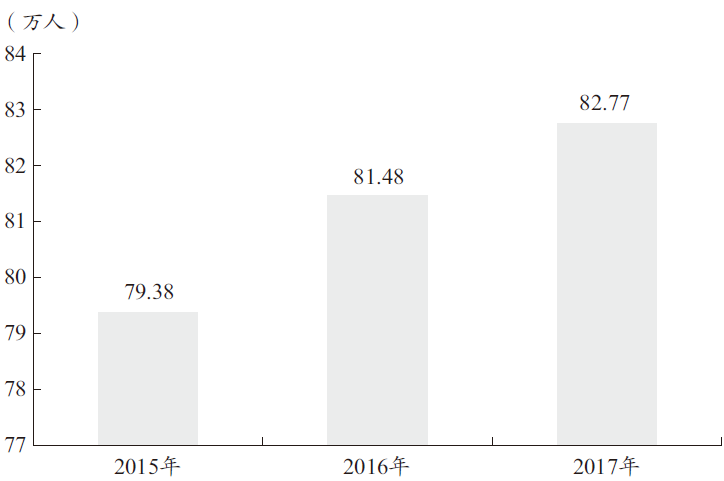
图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。
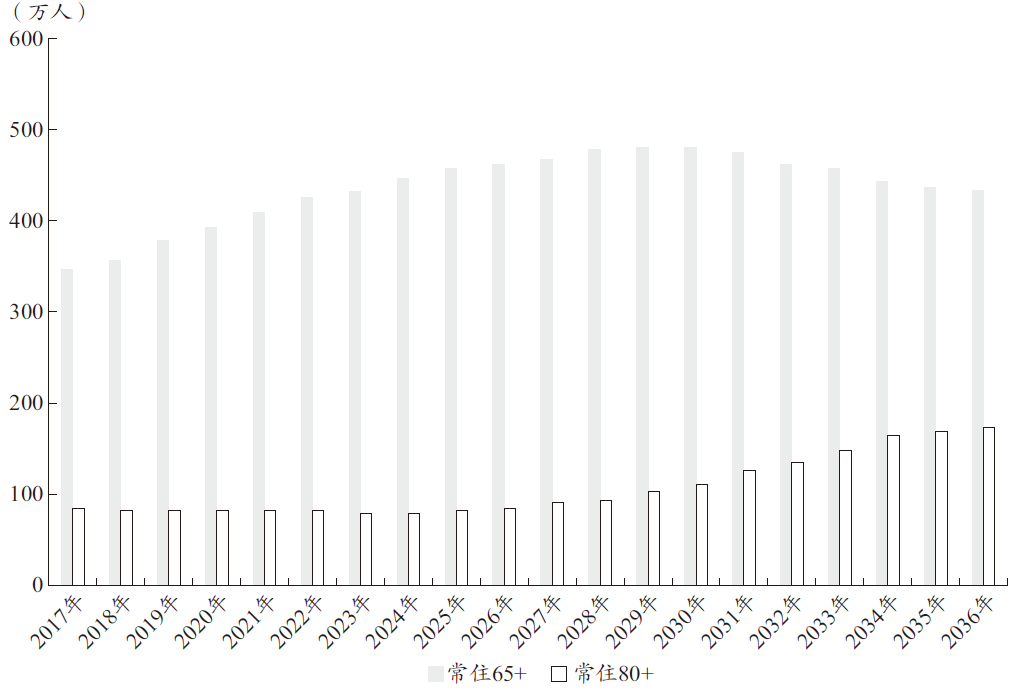
图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
根据上下文,文章第二段括号中应填的数字为( )。
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
根据上下文,文章第二段括号中应填的数字为( )。
A.
537.47
B.
539.12
C.
535.96
D.
544.28
第 47 题
单选题
上海人口老龄化现状和预判
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
2015年,上海市65岁及以上常住人口( )万人。
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
2015年,上海市65岁及以上常住人口( )万人。
A.
318.79
B.
308.18
C.
293.17
D.
297.67
第 48 题
单选题
上海人口老龄化现状和预判
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
2017年,上海市65岁及以上老年人口中,有户籍的比例为( )。
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
2017年,上海市65岁及以上老年人口中,有户籍的比例为( )。
A.
89.34%
B.
87.26%
C.
91.12%
D.
21.8%
第 49 题
单选题
上海人口老龄化现状和预判
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
以下说法中错误的是( )。
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
以下说法中错误的是( )。
A.
外来常住人口占上海市常住人口的40%
B.
外来老年人口增加态势明显是上海人口老龄化特点之一
C.
2016年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口为22.75万人,比上年增加6.53万人
D.
我国国内主要城市均已进入老龄化社会
第 50 题
单选题
上海人口老龄化现状和预判
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
以下说法中正确的是( )。
一、上海人口老龄化现状
上海是我国最早进入老龄化社会的城市,也是我国老龄化程度最高的大型城市。2017年,上海老龄化率达到14.3%(指65岁及以上常住人口占全部常住人口的比重,下同)。按照联合国划分标准,一个国家或地区65岁及以上老人占总人口的7%,即该地区视为进入老龄化社会,上海老龄化率在国内主要城市(北上广深)中老龄化程度是最高的,与国际上大城市相比,也处于较高水平(见表1)。
表1 上海与国内外主要城市老龄化程度

上海人口老龄化呈现以下特点:
一是总量规模大,增量速度快。2017年上海60岁及以上常住人口达到( )万人,65岁及以上的常住人口达到345.78万人,分别比上年增加37.6万人和26.99万人。65岁及以上老年人口增量自2010年第六次人口普查以来首次高于新出生人口(见图1)。

图1 2015—2017年本市新增65岁及以上老年人口和新出生人口比较
二是户籍常住人口老龄化程度显著高于全市水平。2017年,户籍常住人口中65岁及以上老年人口达到315.06万人,户籍人口老龄化率为21.8%,即平均不到5个户籍人口中就有1个65岁及以上的,而60岁以上的占比更高达33.2%,即每不到3个户籍人口中就有1位60岁以上的。因此,本市户籍人口老龄化显著偏高。占全市常住人口40%且整体年龄偏轻的外来常住人口,大幅拉低了全市老龄化程度(见图2)。

图2 2015—2017年本市常住人口老龄化情况
三是外来老年人口开始呈增加态势。随着长期在沪工作的外来常住人口长期定居,以及外来老人来沪为新上海户籍人口子女照料孩子等因素影响,近年来上海外来老年人口规模也开始扩大。2017年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口总量达到30.72万人,比上年增加7.97万人,增长35.0%(见图3)。

图3 2015—2017年本市65岁及以上外来老年人口总量情况
四是80岁及以上高龄老人群体持续扩大。2017年上海80岁及以上老年常住人口为82.77万人,比上年增加1.29万人,占全市60岁及以上老年人口的比重为15.4%(见图4)。

图4 2015—2017年本市80岁及以上老年人常住人口总量情况
二、对上海人口老龄化进程的预判
根据当前上海人口年龄结构、人口机械变动和自然变动情况以及上海城市人口总量规划目标2500万人等因素测算,2030年左右,上海常住老年人口规模将达到历史峰值,约为480万人,常住人口老龄化率为19.2%(见图5)。

图5 2017年—2036年本市常住人口的65岁及80岁以上人口变化情况
人口老龄化问题是上海社会发展过程中必然面临的最严峻挑战,也是必须承担和解决的社会责任,是关系到上海每一个家庭的重大民生问题。因此,有必要尽快提高现有社会公共服务能力,完善社会保障体系并提高保障标准,以适应一个人口迅速老化的社会结构,让每一位老人能够安享一个健康安全而有尊严的晚年。
以下说法中正确的是( )。
A.
预计到2021年上海市常住人口中年龄在65岁及以上的老年人将超过400万人
B.
2016年,上海65岁及以上外来老年人口比上年增加了22.75万人
C.
每3个上海户籍人口中就有1人年龄在65岁以上
D.
外来常住人口的涌入拉高了上海市的老龄化程度
第 51 题
单选题
中国某出口商出口了一批货物,计价结算货币为美元,金额为500万元,9个月后收到货款,为了防范美元汇率下降的风险,以下哪种金融工具可以达到保值的目的?( )
A.
买入9个月期美元看涨期权
B.
买入9个月期美元看跌期权
C.
卖出9个月期美元看跌期权
D.
卖出9个月期美元看涨期权
第 52 题
单选题
如果消费者动用储蓄存款进行消费,货币构成将发生的变化是( )。
A.
M1减少,M2增加
B.
M2不变,M1增加
C.
M2不变,M1减少
D.
M1减少,M2减少
第 53 题
单选题
设立有限责任公司时,股东不可以把________作为出资的财产。
A.
工具和设备
B.
知识产权
C.
特许经营权
D.
土地使用权
第 54 题
单选题
市场机制中最基本的机制是( )。
A.
竞争机制和价格机制
B.
公开机制和自由机制
C.
计划机制和竞争机制
D.
集中机制与分散机制
第 55 题
单选题
根据马克思的利率决定理论,决定利率的基本因素中最基本的是( )。
A.
平均利润率
B.
国家经济政策
C.
社会再生产状况
D.
货币供求和竞争关系
第 56 题
单选题
GDP是衡量经济发展状况的重要指标,下列表述中( )不会计入GDP。
A.
某家庭在春节时购买了500元人民币的烟花
B.
节假日家庭外出旅游支出的费用2万元人民币
C.
家庭雇佣小时工每月支出3000元人民币
D.
甲请假一天,粉刷自家新房节省了300元人工费
第 57 题
单选题
下列选项,不属于利率风险结构决定因素的是( )。
A.
违约风险
B.
到期收益率
C.
税收因素
D.
流动性
第 58 题
单选题
如果国民收入在某个时期内稳定增长,则净投资很可能( )。
A.
为零
B.
持续下降
C.
稳中有降
D.
持续增长
第 59 题
单选题
某银行的平均存款期限小于其平均贷款期限,则其收益与市场利率变化关系是( )。
A.
该银行收益与市场利率强相关
B.
该银行收益与市场利率弱相关
C.
该银行收益与市场利率负相关
D.
该银行收益与市场利率正相关
第 60 题
单选题
通货膨胀是一种商品和服务的价格总水平持续上涨的现象,衡量通货膨胀的指数有许多,下列选项中不是其中之一的是( )。
A.
居民消费物价指数CPI
B.
采购经理指数PMI
C.
GDP平减指数
D.
批发物价指数PPI
第 61 题
单选题
下列有关特别提款权的说法,错误的是( )。
A.
它可以直接用于支付
B.
限定在成员国政府与IMF及各成员国之间发挥作用
C.
没有商品贸易和金融贸易基础
D.
它的价格根据主要发达国家货币汇率加权平均计算得出
第 62 题
单选题
一般来说,在社会自发状态下,公共物品的生产往往低于社会理想的水平,其根本原因在于( )。
A.
公共物品成本过高,无法均摊
B.
公共产品生产较为困难
C.
社会文明程度低
D.
社会成员存在搭便车的倾向
第 63 题
单选题
国债是国家信用的主要形式,政府发行债券的首要动因是( )。
A.
弥补财政赤字
B.
增加政府收入
C.
缩小贫富差距
D.
增加国家储备
第 64 题
单选题
生产一种商品A时,在其他条件不变的情况下,由于生产技术的进步,使得( )。
A.
商品A的供给增加
B.
商品A的供给量减少
C.
商品A的供给减少
D.
商品A的供给量增加
第 65 题
单选题
财政赤字是财政收入未能实现平衡的一种表现,是一种世界性的财政现象,下列弥补财政赤字的融资方式中不会导致基础货币增加的是( )。
A.
直接向中央银行透支
B.
增加政府开支
C.
直接发行通货弥补财政赤字
D.
直接发行债券弥补财政赤字
第 66 题
单选题
银行通常用( )来估价一个活跃交易的债券。
A.
市场收益率
B.
一个债券定价模型
C.
当前市场价格
D.
期货收盘价
第 67 题
单选题
关于经济资本,下列说法不正确的是( )。
A.
经济资本是因内部管理人员根据银行所承担的风险计算的、银行需要保有最低资本量
B.
经济资本是防止银行倒闭的最后防线
C.
经济资本是银行监管当局规定的银行必须持有的资本
D.
经济资本计算所依靠的内部评级包括客户评级和授信条件评级两个方面
第 68 题
单选题
中国实行的汇率制度是( )。
A.
以市场供求为基础的、有管理的浮动汇率制度
B.
以市场供求为基础的、有管理的钉住汇率制度
C.
以市场供求为基础,参考一篮子货币进行调节,有管理的浮动汇率制度
D.
以市场供求为基础,参考一篮子货币进行调节,有管理的钉住汇率制度
第 69 题
单选题
以下特点中不属于完全竞争市场的是( )。
A.
产品同质性
B.
信息有限性
C.
资源流动性
D.
大量买者和卖者
第 70 题
多选题
当消费者和经营者之间围绕消费者权益发生争议时,下列选项中可供选择的解决途径是:
第 71 题
单选题
计算机曾经使用过一种外部存储设备,软磁盘,需要使用软盘驱动器读取。这种磁盘由于数据不确定而被淘汰,以下操作可能造成软磁盘数据丢失的是( )。
A.
放置在不透气的盒子中半年
B.
放在水里10秒
C.
放在强磁场中1分钟
D.
被阳光直射2小时
第 72 题
单选题
下列关于网络带宽的说法错误的是( )。
A.
带宽指在固定的时间可传输的资料数量
B.
高带宽允许更快速的数据传输
C.
带宽容量只取决于上网电脑的运行速度
D.
在数字设备中,带宽有时候以bps表示
第 73 题
单选题
某局域网内可能有部分电脑感染病毒,网管人员此时应首先( ),来避免病毒的进一步扩散。
A.
打开系统的防火墙进行数据包过滤
B.
关闭服务器系统
C.
启动杀毒软件进行查杀
D.
断开感染病毒电脑的物理网络连接
第 74 题
单选题
加密技术通常分为两大类:“对称式”和“非对称式”,以下说法正确的是( )。
A.
对称式加密就是加密和解密使用的不是同一个密钥但位数相同
B.
对称式加密就是加密和解密使用的同一个密钥但位数不同
C.
非对称式加密就是加密和解密所使用的不是同一个密钥
D.
非对称式加密就是加密和解密所使用的是同一个密钥
第 75 题
单选题
一般我们说电脑的型号都会以CPU为主要评价标准,比如:PⅢ800,这里的800指的是( )。
A.
CPU每秒钟可以运行800万条指令
B.
CPU的出厂批次
C.
CPU的时钟频率
D.
CPU支持的最大内存容量
第 76 题
单选题
出于安全和使用的角度,设计一个网站时会考虑使用( )。
A.
功能更好的杀毒软件
B.
安全域名
C.
用数字签名解决篡改或冒充等问题
D.
用业务流分析演示工作流程
第 77 题
单选题
如何使用Word方便地为文章的每页最底部加入版权等信息( )?
A.
更改文字位置
B.
编辑页脚
C.
使用格式刷
D.
设置页面布局
第 78 题
多选题
液晶显示器的技术参数包括( )。
第 79 题
多选题
计算机操作系统的主要功能是资源管理,可管理( )。
第 80 题
单选题
( )的重要作用是将显卡传送来的图像信息在屏幕上显示,它是用户和电脑对话的窗口,它是可以显示用户的输入信息和电脑的输出信息,它与显卡共同组成了电脑的显示系统,是电脑的输出设备。
A.
硬盘
B.
输入输出设备
C.
显示器
D.
CPU
第 81 题
单选题
雷雨过后的空气显得特别清新,其主要原因是:
A.
雷雨过后的空气湿度较大
B.
雷雨过后气压升高
C.
雷雨过后空气中的臭氧含量增加
D.
雷雨过后空气中的浮沉较少
第 82 题
单选题
地震时,某大型超市内发生了骚乱,下列人员中所处位置相对安全的是:
A.
自动电梯上
B.
收银台旁
C.
承重柱旁
D.
奶粉货架旁
第 83 题
单选题
我国经济体制改革的中心环节是:
A.
实行价格体制改革
B.
国有企业改革
C.
进一步完善市场体系
D.
加强宏观经济调控
第 84 题
单选题
生物体能够把自身的一部分组成物质加以分解,释放出其中的能量,并且把分解的终产物排出体外的变化过程,这个过程称为:
A.
分化作用
B.
同化作用
C.
转化作用
D.
异化作用
第 85 题
单选题
白令海峡是________和________的分界线。
A.
非洲 欧洲
B.
亚洲 美洲
C.
非洲 南极洲
D.
美洲 南极洲
第 86 题
单选题
当电气设备发生接地故障,接地电流通过接地体向大地流散,在地面上形成电位分布时,若人在接地短路点周围行走而形成的触电,称为:
A.
两相触电
B.
单相触电
C.
漏电型触电
D.
跨步电压触电
第 87 题
单选题
一列质量较大的火车迎面撞向一列质量较小且静止的火车,则两列火车受到冲击力的情况是:
A.
两列火车均未受到冲击力
B.
两列火车受到的冲击力一样大
C.
质量较大的火车受到的冲击力更大
D.
质量较小的火车受到的冲击力更大
第 88 题
单选题
不谋全局者不足谋一域,不谋万世者不足谋一时。这在哲学上属于:
A.
绝对主义的观点
B.
辩证法的观点
C.
认识事物的量
D.
相对主义的观点 四、时事政策
第 89 题
单选题
2018年10月8日召开的国务院常务会议确定进一步完善________政策,加快________进度,有利于深化供给侧结构性改革,推动实体经济降成本,也有利于应对复杂国际形势,保持外贸稳定增长。
A.
进口增税 增税
B.
进口降税 降税
C.
出口退税 退税
D.
出口免税 免税
第 90 题
单选题
习近平总书记2018年10月10日下午主持召开中央财经委员会第三次会议,强调大力提高我国自然灾害防治能力,全面启动________规划建设。
A.
新藏铁路
B.
川藏铁路
C.
青藏铁路
D.
京藏铁路
第 91 题
单选题
2018年9月26日,交通银行成功发行市场首单基于区块链技术的________资产支持证券。这是交行政为人先,主动拥抱金融科技的创新探索,也是通过该技术打造开放、共享的交行投行生态圈的重大举措。
A.
个人经营性贷款
B.
个人小额信用贷款
C.
个人住房抵押贷款
D.
个人有价单证质押贷款
第 92 题
单选题
首届中国国际进口博览会于2018年________在上海举办,宇宙行近日发布以“工迎进博,行遍寰宇”为主题的专属综合金融服务方案,将借助宇宙行广泛的全球布局,丰富的产品体系和优良的金融服务全面对接,做好进博会的各项金融服务。
A.
11月5日至10日
B.
11月1日至3日
C.
11月5日至7日
D.
11月3日至10日
第 93 题
单选题
2018年全国大众创业万众创新活动周,以“高水平双创,高质量发展”为主题,主会场活动在________开幕。
A.
上海
B.
成都
C.
深圳
D.
北京
第 94 题
单选题
2018年10月9日运抵洋山深水港的首届中国国际进口博览会最大“吨位”展品,来自________的“金牛座”龙门铣床,在办理了进口换单后,于11日上午正式向上海海关报关,上海海关在确认单证信息清晰准确之后,对龙门铣床进行了快速放行。
A.
荷兰
B.
英国
C.
法国
D.
德国
第 95 题
单选题
2018年9月18日,美国政府宣布实施对从中国进口的约2000亿美元的商品加征关税的措施。自2018年9月24日起,加征关税税率为10%,2019年1月1日起,加征关税税率提高到________。美方一意孤行,导致中美贸易摩擦不断升级。为捍卫自由贸易和多边体制,捍卫自身合法权益,中方不得不对已公布的约600亿美元清单商品实施加征关税措施。
A.
30%
B.
25%
C.
20%
D.
15%
第 96 题
单选题
Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
What is the main purpose of the Open Networking Foundation
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
What is the main purpose of the Open Networking Foundation
A.
To set new standards for computer networking.
B.
To promote cloud computing.
C.
To enhance the capabilities of network engineers.
D.
To make networks less expensive to build and operate.
第 97 题
单选题
Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
“Orchestrate” in Par
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
“Orchestrate” in Par
A.
5 probably means ______. xuanxiang_tag_enameA. integrate
B.
conform
C.
comply
D.
harmonize
第 98 题
单选题
Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
The possible benefits of the standardized technologies will not include ______.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
The possible benefits of the standardized technologies will not include ______.
A.
improved computer security
B.
networks that are less expensive to build
C.
software for data rush hours
D.
growing use of computing in the e-commerce market
第 99 题
单选题
Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
Which of the following is NOT true about OpenFlow according to the passage
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
Which of the following is NOT true about OpenFlow according to the passage
A.
It is an initiative of Nick McKeown and his colleagues.
B.
It will trigger new innovations in the field of cloud computing.
C.
It is meant to help with the storing and processing of information on computers.
D.
It deviates from the traditional Internet.
第 100 题
单选题
Acknowledging that so-called cloud computing will blur the distinctions between computers and networks, about two dozen big information technology companies plan to announce a new standards-setting group for computer networking. The group, to be called the Open Networking Foundation, hopes to help standardize a set of technologies pioneered at Stanford and the University of California, Berkeley, and meant to make small and large networks programmable in much the same way that individual computers are.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
It can be inferred from the passage that ______.
The changes, if widely adopted, would have implications for global telecommunications networks and large corporate data centers, but also for small household networks. The benefits, proponents say, would be more flexible and secure networks that are less likely to suffer from congestion. Someday, they say, networks might even be less expensive to build and operate. The new approach could allow for setting up on-demand “express lanes” for voice and data traffic that is time-sensitive. Or it might let big telecommunications companies, like Verizon or AT & T, use software to combine several fiber optic backbones temporarily for particularly heavy information loads and then have them automatically separate when a data rush hour is over. For households, the new capabilities might let Internet service providers offer remote services like home security or energy control.
The foundation’s organizers also say the new technologies will offer ways to improve computer security and could possibly enhance individual privacy within the e-commerce and social networking markets. Those markets are the fastest-growing uses for computing and network resources. While the new capabilities could be crucial to network engineers, for business users and consumers the changes might be no more noticeable than advances in plumbing, heating and air-conditioning. Everything might work better, but most users would probably not know — or care — why or how.
The members of the Open Networking Foundation will include Broadcom, Brocade, Ciena, Cisco, Citrix, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, Ericsson, Facebook, Force10, Google, Hewlett-Packard, I.B.M., Juniper, Marvell, Microsoft, NEC, Netgear, NTT, Riverbed Technology, Verizon, VMware and Yahoo. “This answers a question that the entire industry has had, and that is how do you provide owners and operators of large networks with the flexibility of control that they want in a standardized fashion,” said Nick McKeown, a professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Stanford, where his and colleagues’ work forms part of the technical underpinnings, called OpenFlow.
The effort is a departure from the traditional way the Internet works. As designed by military and academic experts in the 1960s, the Internet has been based on interconnected computers that send and receive packets of data, paying little heed to the content and making few distinctions among the various types of senders and receivers of information. The intelligence in the original Internet was meant to reside largely at the end points of the network — the computers — while the specialized routing computers were relatively dumb post offices of various size, mainly confined to reading addresses and transferring packets of data to adjacent systems. But these days, when cloud computing means a lot of the information is stored and processed on computers out on the network, there is growing need for more intelligent control systems to orchestrate the behavior of thousands of routing machines. It will make it possible, for example, for managers of large networks to program their network to prioritize certain types of data, perhaps to ensure quality of service or to add security to certain portions of a network. The designers argue that because OpenFlow should open up hardware and software systems that control the flow of Internet data packets, systems that have been closed and proprietary, it will cause a new round of innovation focused principally upon the vast computing systems known as cloud computers.
It can be inferred from the passage that ______.
A.
people will have a better understanding of the distinctions between computers and networks thanks to cloud computing
B.
cloud computing will involve more routing computers than the traditional internet
C.
with the setting of new standards, operators of large networks will have more flexibility of control
D.
the Open Networking Foundation will be led by Stanford and the university of California, Berkeley